United States GDP Growth 2025: Trends, Challenges, and What It Means for the Economy
Meta Description (SEO):
Explore how U.S. GDP growth performed in 2025, what’s driving expansion and slowdown, and what it means for consumers and investors. Key insights for the American economy.
Keywords: United States GDP Growth 2025, U.S. economic growth, GDP forecast, U.S. economy 2025, consumer spending, tariffs impact
U.S. GDP Growth in 2025: A Mixed Picture
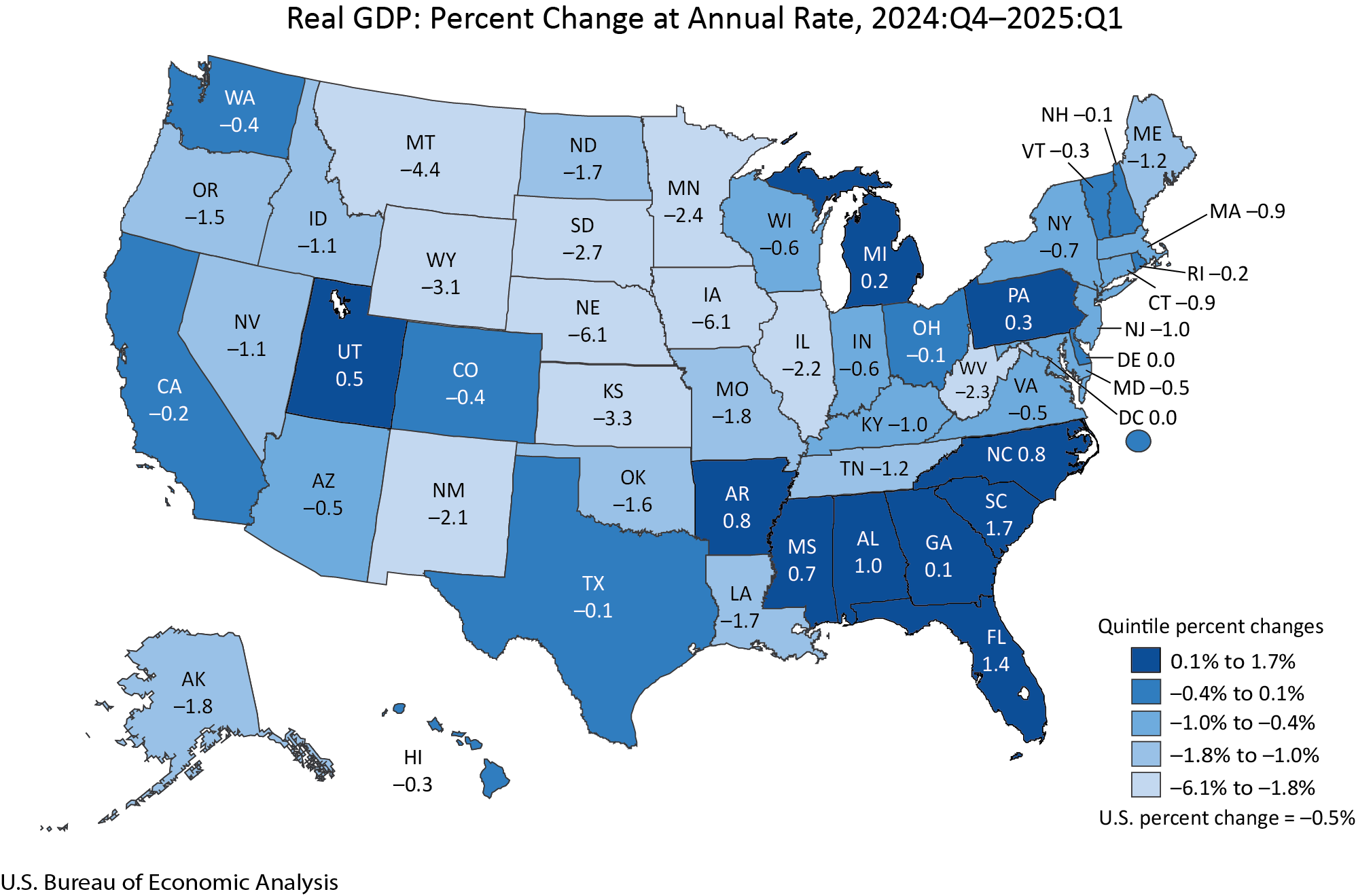
The United States GDP growth in 2025 has shown mixed signals, reflecting a complex economic landscape shaped by consumer demand, corporate investment, and policy uncertainty. Overall, growth has proved more resilient than many analysts anticipated earlier in the year, though activity has cooled compared with post‑pandemic rebounds.
According to official estimates and data models, the U.S. economy expanded at an annualized rate around 3.0% in the second quarter of 2025, significantly stronger than early predictions of modest growth. This rebound followed a contraction in the first quarter, highlighting the economy’s ups and downs throughout the year. Trading Economics+1
Economists from major institutions — including Vanguard and S&P Global — forecast full‑year GDP growth of roughly 1.9% to 2.0% for 2025, a modest pace that reflects persistent headwinds from global trade tensions, high interest rates, and uncertainty surrounding fiscal policy. Vanguard+1
Drivers of U.S. Economic Growth
Consumer Spending and Business Investment
One of the most important drivers of U.S. GDP growth in 2025 has been consumer spending, which supported expansion throughout the spring and summer. Higher household consumption helped offset weaker government expenditure and slower export growth. Trading Economics
Business investment also contributed to GDP performance, as companies increased capital spending in select sectors, particularly in technology and services industries. This reflects broader trends in the American labor market and corporate confidence.
Federal Reserve Policy and Inflation
Monetary policy has played a central role in shaping economic growth. The Federal Reserve’s cautious stance on interest rates — maintaining relatively high rates to control inflation — has tempered borrowing and investment but helped avoid overheating in key sectors.
While inflation has moderated compared with previous years, it remains above the Fed’s 2% target, influencing consumer prices and purchasing power. The interplay between inflation, wage growth, and interest rates continues to affect economic activity and GDP outcomes.
Challenges Facing the Economy
Slower Growth Expectations
Despite resilience in certain quarters, many forecasters believe that overall growth will slow as 2025 progresses and into early 2026 due to structural and policy challenges, including tariff uncertainty and fiscal constraints. The Conference Board
Tariff Impact and Trade Policy
Trade tensions and tariff policies implemented in 2025 have introduced headwinds for economic growth. While aimed at protecting domestic industries, higher tariffs have raised input costs for U.S. manufacturers and reduced export competitiveness. These factors contribute to downward pressure on GDP growth estimates and add volatility to the broader economy. Wikipedia
How GDP Growth Affects Americans
GDP growth matters to everyday Americans because it influences job creation, wages, consumer prices, and investment returns. Moderate growth often correlates with sustained employment gains, though in 2025 the labor market has shown signs of cooling, with the unemployment rate rising to a four‑year high of 4.6% in late 2025. Financial Times
Consumer confidence and retail spending are directly impacted by economic growth trends. Stagnant or slowing GDP can lead households to reduce discretionary spending, affecting sectors like retail, hospitality, and services. Conversely, stable GDP supports steady job growth and increases in personal income.
Looking Ahead: GDP Forecast for 2026
Most economic forecasts anticipate continued moderate growth into 2026, with GDP expanding at around 2.0%–2.3%. This is slightly above 2025 projections but still below historical pre‑pandemic averages. S&P Global
Analysts point to several factors that could influence growth next year, including:
- Monetary Policy Adjustments: Potential rate cuts by the Fed could stimulate borrowing and investment if inflation continues to ease.
- Labor Market Dynamics: A more robust employment picture could boost consumer spending and confidence.
- Global Economic Conditions: Recovery in international markets and easing trade tensions would benefit U.S. exports.
Conclusion: A Year of Resilience and Transition
The United States GDP growth in 2025 reflects a year of resilience and adaptation. After early contraction and volatility, the economy managed to expand at a solid pace in parts of the year, driven by consumer demand and investment. However, slower growth expectations, tariff pressures, and monetary policy uncertainties signal a cautious outlook.
For Americans — from consumers to investors — understanding these GDP trends is essential for planning spending, saving, and investment strategies as the economy navigates evolving domestic and global challenges.







